Master ESOP Rules and Compliance
Employee Stock Option Rules Explained: A Practical Guide to Employee Stock Options and Regulatory Requirements
Introduction to Master ESOP Rules and Compliance
Stock options have emerged as one of the most popular long-term reward systems in attracting, retaining and motivating employees especially in companies that are growth-driven and companies that operate in the knowledge-based industry. Employers and employees should be well versed with the regulations of employee stock option rules, the rules and regulations of such plans in practice as well as regulatory frameworks to use them effectively. Correct interpretation of concepts of employee stock options is necessary as a means of preventing compliance risks, tax inefficiencies and misalignment of expectations.
This article is a one-stop employee stock options guide, describing the mechanics of employee stock options, the most significant rules that govern their issuance and exercise, and the employee stock option regulation environment overall. The debate is presented in formal, understandable business English and can be read by founders, executives, human resource specialists, finance departments, and employees assessing the business on equity-based compensation.
Employee Stock Option Explained in Practical Terms
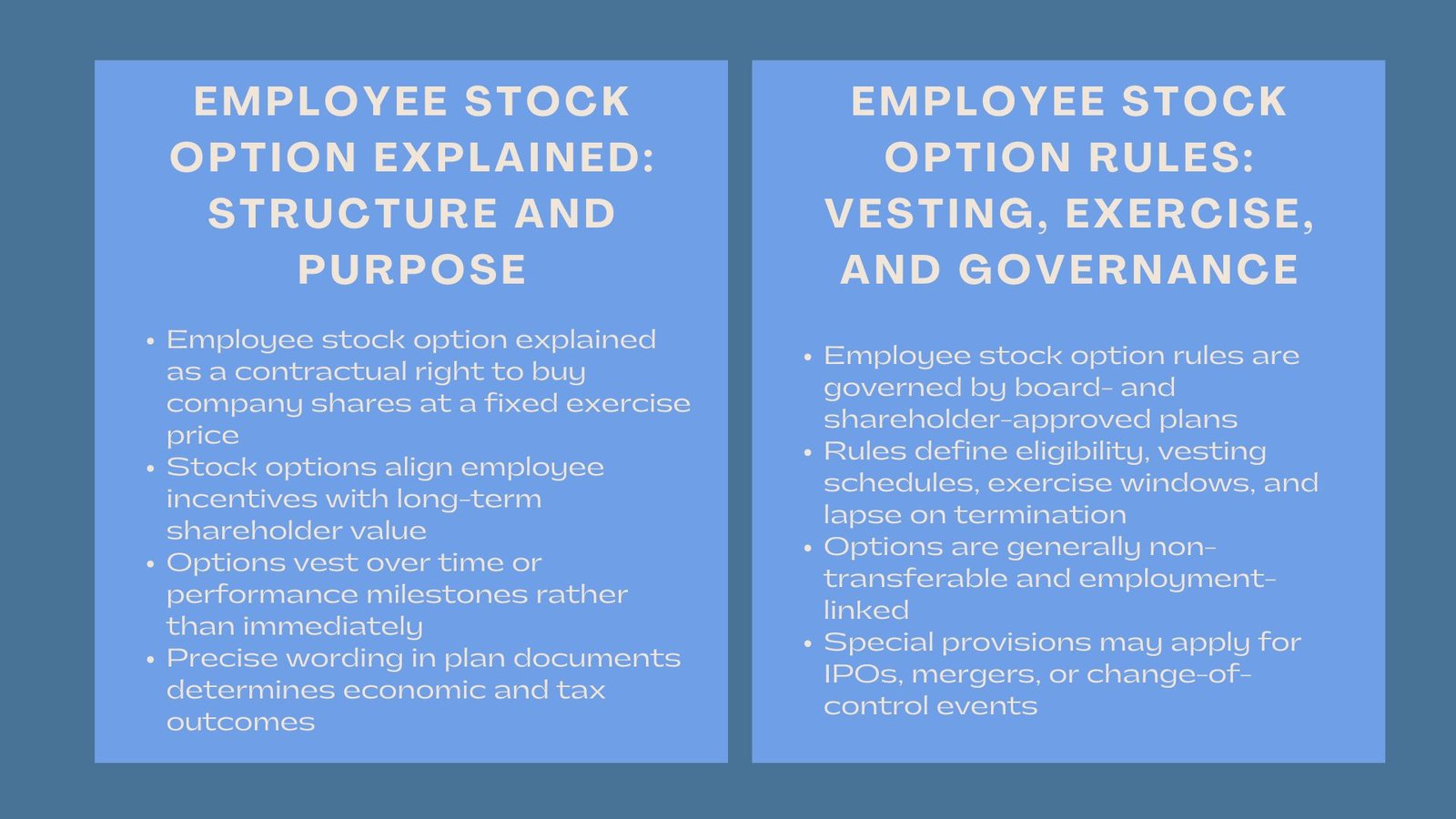
When the employee stock option explained clearly, an employee stock option is a right that is a contract which the company offers to an employee of the company enabling the employee to acquire company shares at a pre-agreed price, which is called exercise or strike price, over a period of time. The fundamental aim of this framework is to ensure that the incentives of the employees coincide with the creation of shareholder value.
Most of the employee stock option rules do not make options immediately exercisable. They rather become vested either through time basis or through performance milestones. Vesting is a way of making employees share in the company by their service or contribution. After vesting the employees are allowed to exercise their options, depending on the terms of the plan and regulatory provisions.
It is important to have an appreciation of how employee stock options have been explained in the employment contracts and the plan documentation because a slight variation in the wording can have a significant impact on the economic results and the tax treatment.
Core Employee Stock Option Rules Governing Option Plans
Employee stock option rules are founded on the plan documentation that is endorsed by the board of directors of the company and in most jurisdictions by shareholders. These regulations determine the eligibility, vesting plans, exercising times, lapse terms and treatment at the end of working.
One of the key principles that are shared in employee stock options guidelines is the fact that stock options are generally not transferable and tied to employment. Lapses of the options may be as soon as an employee leaves the company or as a short post-termination exercise period. The regulations also dictate whether options accelerate in case of events like change of control, merger or IPO.
Employee stock option regulation are well laid down to enable a balanced balance between motivation and dilution management and shareholder interests, in view of governance.
Employee Stock Options Guide to Vesting and Exercise
An employee stock options guide should also be a complete guide that covers the aspects of vesting and exercise mechanics because these aspects are the determining factors of being able to realize value. Vesting plans are typically time-based e.g. four year vesting with one year cliff, but performance based vesting is becoming a popular practice in the compensation of senior executives.
Upon the options vesting, the employees can use them by paying the exercise price and other taxes that may be charged. The time of exercise is a tactical move which depends on liquidity outlook, share price prospects, regulatory or taxation. The stock option regulations concerning employees usually set deadlines under which the exercise can be done especially upon termination of employment.
The knowledge of the vesting and exercise provisions is one of the pillars of an employee stock options guide because most of the time, failure to understand this area results in loss of value.
Employee Stock Option Regulation and Legal Frameworks
The control of employee stock options at different jurisdictions differs but is broadly encompassed in the company law, securities regulation, tax law, and employment law. These laws specify the manner in which options can be awarded, reported, estimated and taxed.
Employee stock option regulation in most countries must be formal, which needs substantial employee disclosure and periodic reporting. In the case of private firms, valuation regulations are usually implemented to make sure that options are not exercised at a discount, which may attract undesirable tax effect. In the case of listed companies, there are normally other market disclosure and shareholder approval requirements.
Meeting employee stock option regulation is not a choice. Lack of compliance may lead to fines, nullity of option-grants, or unforeseen tax expenditures on the part of both employers and employees.
Tax Considerations Within Employee Stock Option Rules
Tax considerations are part and parcel of rules governing employee stock options though tax treatment varies across jurisdictions. Taxation can be on a grant, a vesting, exercise or a sale of shares based on the structure of the plan and laws of place.
Most systems have employee stock options which are taxable at the time of exercise, the difference between the market value of the shares and the exercise price. Certain jurisdictions are offering special treatment of tax regimes to qualifying employee stock options, but with severe regulatory requirements. Effective plan design and communication with employees requires understanding of the interaction between employee stock option regulation and the tax law.
A properly designed employee stock options guide must always invite the employee to consult with an independent tax advisor since individual situations may have great influence over the results.
Accounting and Valuation Under Employee Stock Option Regulation
On the accounting side, employee stock options have to be valued at fair value at the time of granting, and expensed during the times that they are vested. Financial reporting standards have ingrained this requirement and are supported by regulation of employee stock options.
Black-Scholes models or binomial models are typical valuation models that are utilized to estimate option fair value. These appraisals have impacts on reported profitability, equity reserves and investor perceptions. This therefore requires firms to combine employee stock option regulations and sound valuation governance and financial reporting practices.
Employee Stock Options Guide for Employers and Employees
A good employee stock options guide has two clients at the same time. To employers, it offers a model on how to create compliant, competitive and sustainable equity incentive plans. To employees, it describes the rights, obligations, risks, and possible rewards in a clear manner.
Effective expression of employee stock option policies minimizes conflicts, builds trust, and reinforces the motivation effectiveness of equity reward. When employees have knowledge of the functioning of the stock options, then they will tend to appreciate them as they deserve and put effort towards achieving long-term corporate objectives.
Conclusion
Finally, employee stock option regulations establish the legal, financial, and operational form of the equity-based compensation, and employee stock option elaborated concepts make sure that the participants comprehend how the value can be created and achieved. An effective employee stock options guide, formally designed, also helps in filling the breach between technical control and real decision-making in assisting compliance and strategic fit.
Since the regulation of employee stock options is still undergoing change in accordance to the market trends as well as regulatory review, it is the responsibility of both the company and the employees to be updated. Knowing these principles will help organizations to leverage on stock options as an effective incentive tool in safeguarding stakeholders and long term value creation.