Understanding ESOP in Share Markets
Understanding ESOP in Share Markets
Introduction
Equity-based compensation is one of the most important strategic instruments of the contemporary capital markets that allow organizations to equate the incentives of the employees with the long-term corporate performance. Of these mechanisms, the concept of esop in the share market has continued to become more relevant to more listed and non-listed companies aiming at attracting, retaining and motivating the key talents. Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) refers to the strategy of giving employees a chance to contribute to the process of value creation in the company, which makes them long-term rather than wage earners.
With the ever-increasing regulatory level of scrutiny and financial disclosure, during scrutiny, companies need to employ ESOPs with high level of discipline. These are setting up a full-fledged employee share option plan, making sure that it is up to regulatory standards, and externalizing an experienced esop valuation consultant to help in fair valuation. ESOPs, therefore, have structural, valuation and governance implications which boards, management, investors and employees need to know.
This article aims at discussing in detail ESOPs, their definition in the stock market, the legal and contractual basis, the valuation procedures and their role in ensuring corporate governance and long-term value generation.
Understanding ESOP Meaning in Share Market
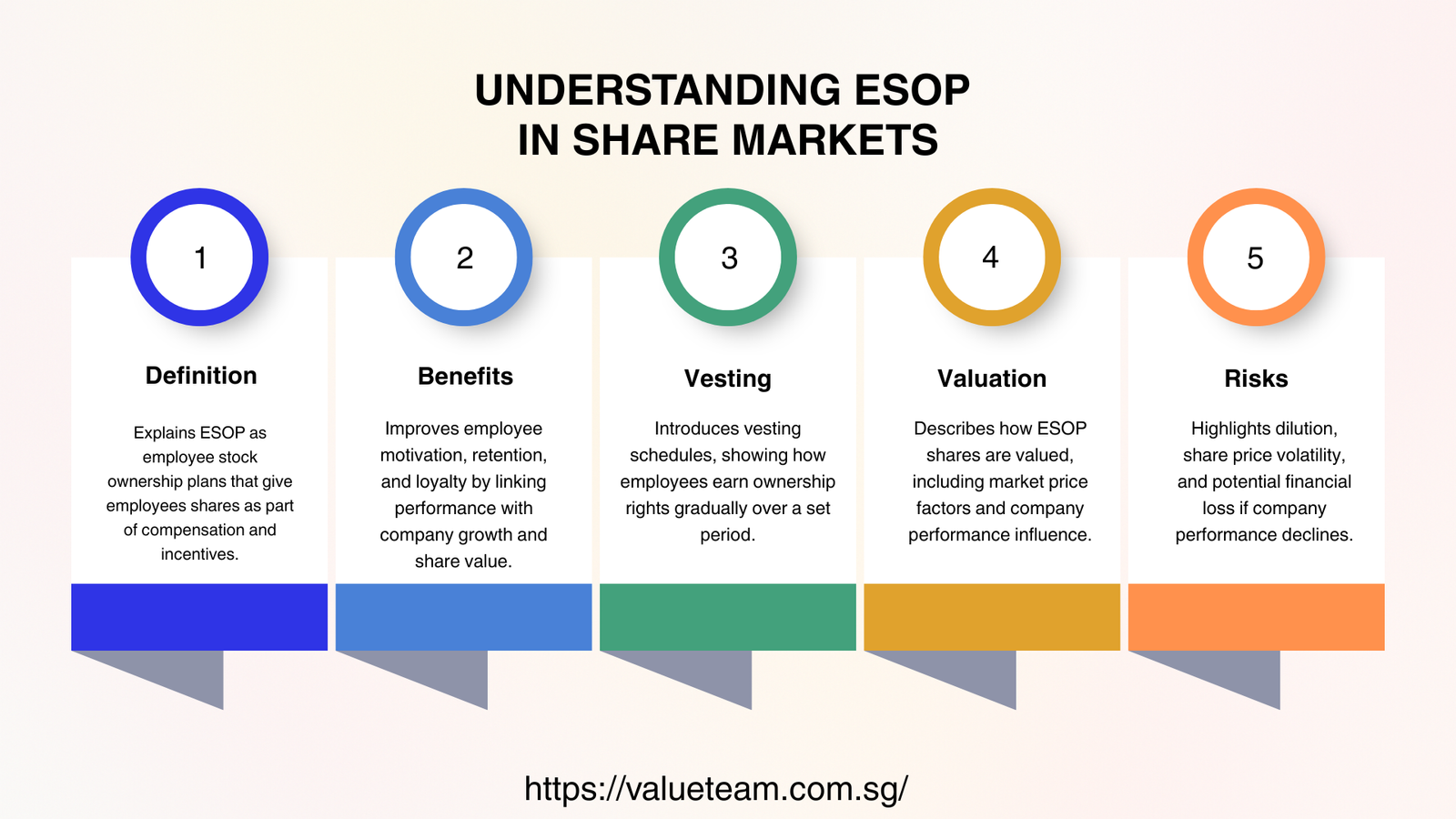
The esop meaning in share market can be described as an organized plan of compensation where employees are entitled but not compelled to acquire the shares of the company at a fixed price after a set period of time. Public companies, private businesses, and start-ups have embraced ESOPs to encourage employee ownership and shareholder interests.
Capital market wise, ESOPs are an equity based compensation in the form of deferred, and not cash outlays. The structure will enable companies to maintain the liquidity and encourage employees to concentrate on long-term growth and value creation.
Securities authorities and rules of stock exchange usually govern ESOPs in listed companies to make them transparent and fair. Even in the case of private businesses, ESOPs are equally significant, but more valuation discipline is needed since the market price cannot be observed.
ESOPs Strategic Objectives
Icentive alignment is the main aim of ESOPs. With equity-based rewards, the companies make employees think and act as owners, which helps them to think long-term, take risks and waste slow.
Talent retention is another fundamental feature of esop meaning in share market. Vesting plans motivate employees to stay longer with the company, which lowers the turnover rate and safeguards organizational knowledge. ESOPs are also an effective hiring instrument in very competitive firms where financial rewards may not be adequate.
Governance wise, ESOPs aid in the creation of performance based culture and enhance accountability. Such benefits, however, can be achieved in as much as ESOPs are planned and managed in a transparent manner.
Employee Share Option Agreement: Contractual and Legal basis
Any ESOP is supported by a properly written employee share option agreement. This agreement stipulates the rights, duties and terms of the granting and exercising of stock options. In the absence of a definite and implementable agreement, ESOPs can put companies at legal, financial, and reputational risk.
The employee share option favor is generally described by eligibility standards, vesting timetables, workout costs, termination, and succession of control. It also covers corporate activities involving mergers, acquisitions and restructuring that can impact option holders.
Regulatory wise, the deal has to be in line with securities laws, labor regulatory laws and relevant accounting rules. In the case of public companies, disclosure rules also increase the significance of accuracy and transparency in such contracts.
ESOP Governance Contemplations
In addition to legal compliance, the employee share option agreement is very critical towards corporate governance. Documentation is clear and consistent so that there is fair treatment within the groups of the employees and reduced internal conflicts and outside measures.
The boards and compensation committees are mandated to sanction ESOP structure, dilution effect and alignment with shareholders interests. Ill-designed agreements can lead to over-dilution, incentives being out-of-line, or having unintended financial effects.
Strong internal controls, regular reviews and external checks are thus the key to upholding the integrity of governance.
Valuation Significance of ESOP Implementation
An effective ESOP implementation is based on valuation. Proper valuation will make sure that the stock options are awarded at a fair value and will benefit the employees and the shareholders. It is here that experience of an esop valuation analyst would be invaluable.
The esop valuation analyst values the equity instruments based on the accepted valuation techniques. These appraisals have direct implications on financial reporting, taxation, as well as the sense of fairness on the part of the employees.
Regulatory fines and loss of stakeholders are some of the consequences of unsupported or inaccurate valuations that may cause audit problems. Valuation is therefore not just a technical process but one of the functions of governance.
ESOP Valuation Analyst Job Description
As an esop valuation analyst, an individual uses professional judgment, market data, and financial theory to make estimates around the value of stock options of employees. This position needs a high level of understanding of valuation standards, accounting frameworks and dynamics in the industry.
The analyst analyses the performance of the company, its growth opportunities, capital structure, volatility, and its market counterparts. Valuation complexities are more in the case of private companies because of the lack of liquidity and non-observable share prices.
A large number of regulatory frameworks regulate that ESOP valuations are prepared or analyzed by professional persons of independent nature. Having an esop valuation analyst with proper qualifications helps a lot in increasing credibility and audit defensibility.
Valuation Methodologies of ESOPs
In ESOP valuation a number of valuation techniques are regularly employed namely a number of income-based methods, a number of market-based approaches and option pricing models. The methodology used relies on the maturity of companies, the availability of data and the regulations.
Some stock options that are valued using option pricing models include Black-Scholes or binomial models. These models involve volatility, expected life and risk-free interest rates assumptions.
The esop valuation analyst will have to make sure that all his or her assumptions are sensible, documented and that they are in line with the market evidence. In order to evaluate the valuation robustness sensitivity analysis is usually used.
Implications of Accounting and Financial Reporting
ESOPs directly affect the financial statements in the accounting perspective. The fair value that is calculated by the esop valuation analyst is treated as an expense of compensation to the employees during the time they successfully manage to hold on to their vests.
To be able to report on financial matters and analyze earnings properly, it is thus important to have an understanding of esop meaning in share market. The costs of ESOP affect rates of profits, performance indicators, and investor opinions.
Transparency and investor trust prescribe the provisions of accounting standards, which force the disclosure of specifics of ESOP terms, valuation assumptions, and expenses recognition.
Tax and Regulatory Educations
ESOPs have heavy taxation on both the employer and the employees depending on the jurisdiction and structure of the transaction. The treatment of tax is determined by the factors like, grant date, exercise, and holding period.
The employee share option agreement usually stipulates tax obligations and the compliance rules. Efficient communication of the tax implications allows the employees to make wise decisions and the chances of conflict are minimized.
ESOPs are under greater scrutiny by regulators to eliminate abuse and provide fair treatment and thus proper valuation and documentation is necessary.
Public and Private Company ESOPs
The use of esop in the share market is different in both the public and the private companies. Public companies have the advantage of clear market prices but are required to have greater disclosure and compliance requirements.
Start-up firms are dependent on ESOP as a source of talent. The valuation issues are however more difficult owing to illiquidity and lack of financial history which further puts dependence on an esop valuation analyst.
Both situations demand strict management, precise contracts and strong valuations.
Risks and Common Pitfalls
Although ESOPs may have beneficial points, they have risks associated with them.. The terms of employee share option agreement can either cause dissatisfaction among the employees or arbitral court cases. The excessive optimism in valuations may inflate the compensation cost and may cause greater impairment risk.
A misconception in the meaning of esop in share market can also lead to unrealistic expectations of the employee about the liquidity and generation of wealth. Education and straightforward communication are thus important.
These risks are alleviated by strong governance, independent valuation and periodic reviews.
Strategic Value of ESOPs
The proper implementation of the ESOPs leads to the long-term value addition since it builds the culture of ownership, increases retention, and achieves the alignment of the workforce and shareholders goals.
The information offered by the esop valuation analyst can also be used to make more overall strategic choices, such as capital planning, mergers, and talent management. ESOPs are therefore developed as a form of compensation, rather than a strategy of growth.
Future Trends in ESOPs
With the growing nature of knowledge-based business, ESOPs will likely have a greater contribution in providing compensation. The innovation of valuation analytics, harmonization of regulations, and the standards of governance will also enhance professionalisation in the implementation of ESOP.
An effective interpretation of the share market esop meaning with sound employee share option agreement structures and involvement of esop valuation analysts will also prove critical with the changing stakeholder expectations.
Conclusion
ESOPs are an effective tool of aligning staff interests with long-term value creation in the corporation. Having a clear understanding of the meaning of esop in a share market allows the company to come up with equitable, transparent and strategically viable equity compensation plans. The legal and governance basis of the employee share option agreement is provided by the employees share option valuation analyst, and the valuation is made correct and defensible.
ESOPs are beneficial when they are backed with robust governance, strict valuation, and open communication, raising investor confidence, as well as employee engagement and enterprise sustainable value. Since the equity-based compensation is yet to develop, the discipline of the ESOP execution will be a crucial aspect of the contemporary corporate strategy.